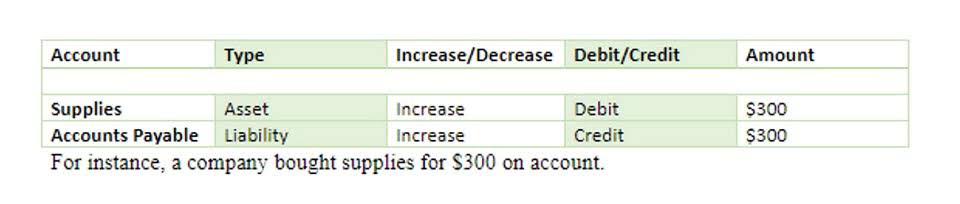
You should consult your own legal, tax or accounting advisors before engaging in any transaction. The content on this website is provided “as is;” no representations are made that the content is error-free. They have estimated the machine’s useful life to be eight years, with a salvage value of $ 11,000.

Emagia has processed over $900B+ in AR across 90 countries in 25 languages.
- This polarization is likely the result of the uneven pace of urban development during periods of rapid urbanization and industrialization.
- The problem states that depreciation expense under the straight-line method in Year 5 is $3,000.
- Further, this approach results in the skewing of profitability results into future periods, which makes it more difficult to ascertain the true operational profitability of asset-intensive businesses.
- This method assumes that assets tend to lose their value more rapidly in their initial years of operation and gradually slow down in depreciation over time, which accounting teams track with a depreciation journal entry.
- It is particularly suitable for assets whose usage varies significantly from year to year.
- Since the depreciation is done at a faster rate (twice, to be precise) than the straight-line method, it is called accelerated depreciation.
For instance, if an asset’s market value declines faster than anticipated, a more aggressive depreciation rate might be justified. Conversely, if the asset maintains its value better than expected, a switch to the straight-line method could be more appropriate in later years. This method helps businesses save on taxes early on by showing higher expenses in the first few years. Understanding the tools available for double declining balance depreciation can greatly enhance your financial management skills.

Common Challenges During Calculation
This method is often used for things like machinery or vehicles that lose value quickly at first. MACRS, or Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery Interior Design Bookkeeping System, is the standard depreciation method used for most tangible property placed in service after 1986. It allows accelerated depreciation, meaning larger deductions early in the asset’s recovery period to reflect asset wear and economic reality.
Understanding Double Declining Balance Depreciation
Owning assets in a business inevitably means depreciation will be required since nothing lasts forever, especially for fixed assets. It is therefore specifically important for accountants to understand the different methods used in depreciating assets as this constitutes an important area to be taken care of by accounting professionals. Salvage QuickBooks value is the estimated resale value of an asset at the end of its useful life.
This higher initial depreciation aligns with the rapid decrease in the car’s value and the heavy use in the early years. A variation on this method is the 150% declining balance method, which substitutes 1.5 for the 2.0 figure used in the calculation. The 150% method does not result in as rapid a rate of depreciation at the double declining method. DDB depreciation is less advantageous when a business owner wants to spread out the tax benefits of depreciation over a product’s useful life.
Double Declining Balance Method (DDB)
The DDB method offers several advantages, particularly for businesses with assets that depreciate quickly. By prioritizing higher depreciation in the early years, it aligns financial records with real-world asset usage and delivers multiple benefits. We just looked at the double declining balance depreciation method, the others shouldn’t take too long to master.
DDB Depreciation Formula

The “double” means 200% of the straight line rate of depreciation, while the “declining balance” refers to the asset’s book value or carrying value at the beginning of the accounting period. Accelerated depreciation methods front-load expense recognition, impacting asset valuation and financial reporting. Proper journal entries track depreciation, affecting accumulated depreciation accounts. Reporting these accurately on financial statements ensures compliance and transparent asset management.
By incorporating depreciation into financial models, businesses can plan for future investments, manage budgets more effectively, and comply with accounting standards. DDB is a specific form of declining balance depreciation that doubles the straight-line rate, accelerating expense recognition. Standard declining balance uses a fixed percentage, but not necessarily double. Both methods reduce depreciation expense over time, but DDB does so more rapidly.
The IRS provides detailed classifications under the Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System (MACRS). Eligible assets must be placed in service and meet recovery period guidelines, generally ranging from 3 to 39 years. Moreover, the TCJA removed the requirement that double declining balance formula bonus depreciation be limited to new property, allowing used property to qualify. These changes have encouraged increased capital investment by lowering the upfront tax burden on businesses. Common classes include 3, 5, 7, 15, and 39 years, depending on the asset type. Real property generally uses longer recovery periods, such as 27.5 years for residential rental property and 39 years for nonresidential buildings.